Resident Program - Case of the Month
December 2021 – Presented by Dr. Jake Donnelly (Mentored by Dr. Irfan Chaudhry)
Discussion
In childhood, medulloblastoma is the most common malignant tumor. The tumor generally occurs in the first 20 years of life, with the median age being 9 years. Medulloblastoma has a slight predominance in males ~ 2:11.
Medulloblastoma is an embryonal neuroepithelial tumor that arises in the cerebellum or dorsal brainstem3. The mass can cause an increase in intracranial pressure due to obstruction of the 4th ventricle, which can lead to headache, lethargy, and vomiting3. Imaging would reveal a midline homogenous mass with peritumoral edema. On gross examination, the mass is a gray-pink, soft friable mass. Treatment can be via surgery or radiation. Medulloblastoma has a 50-80% 5-year survival rate4. Medulloblastoma is sorted into classes based on genetics and histologic findings.
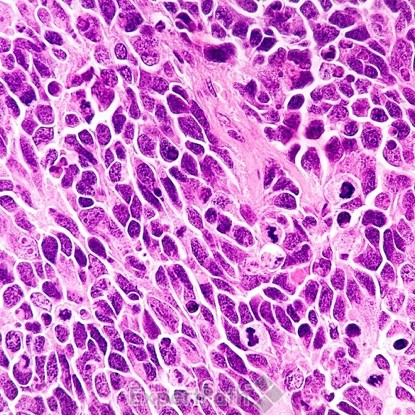
The four histologic based classes are classic, desmoplastic/nodular, medulloblastoma with extensive nodularity, and large cell/anaplastic.
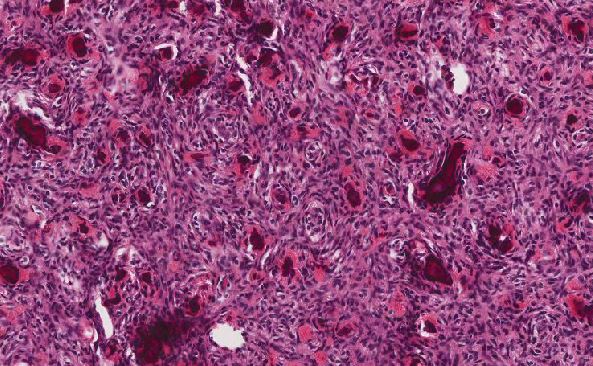
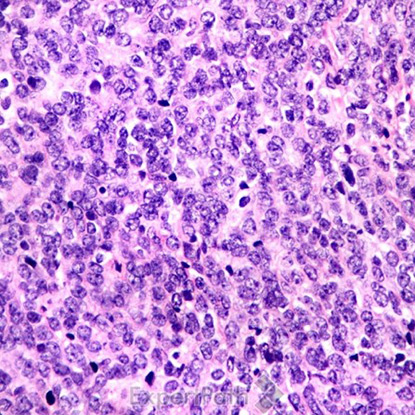
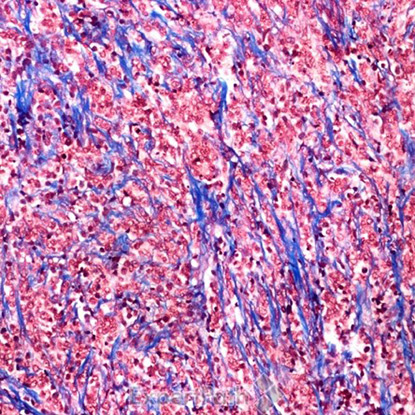
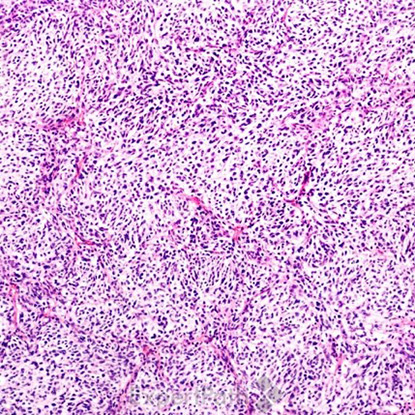
Classic medulloblastoma is composed of a small blue round cell tumor with a syncytial arrangement of densely packed undifferentiated cells2 (Figure 1). Desmoplastic/Nodular medulloblastoma shows densely packed undifferentiated cells with pleomorphic nuclei that are hyperchromatic. There is a dense intercellular reticulin network1 (Figure 2). Medulloblastoma with extensive nodularity demonstrates expanded lobular architecture with reticulin free nodular zones1 (Figure 3). Anaplastic medulloblastoma demonstrates marked nuclear pleomorphism, a high mitotic/apoptotic count, and nuclear molding4 (Figure 4).
The genetic classifications of medulloblastoma are WNT activated, SHH activated, non WNT/non SHH activated medulloblastoma group 3 or group 42.
Unfortunately, due to the decedents age and prior normal health, the medulloblastoma was not discovered until the postmortem examination. The cause of death was acute cerebellar hemorrhage, due to medulloblastoma. Covid-19 was listed as other significant cause of death.
Works Cited:
- Polydorides, Alexandros. “Medulloblastoma.” ExpertPath, 28 Oct. 2018.
- Ramaswamy V, Taylor MD. Medulloblastoma: From Myth to Molecular. J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jul 20;35(21):2355-2363. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.72.7842. Epub 2017 Jun 22. PMID: 28640708.
- Schaberg, Kurt. “CNS Tumors.” Kurts Notes, 4 Mar. 21AD.
- Singh, Nirupama. “Medulloblastoma.” Pathology Outlines - Medulloblastoma, 19 July 2021.

 Meet our Residency Program Director
Meet our Residency Program Director